
Here’s the Reason GM Created a Gas Exhaust for Electric Vehicles
Cadillac
Subscribe to The Drive’s daily newsletter
Stay updated with the latest car news, reviews, and features.
Every few months, it seems that someone attempts to add an exhaust system to an electric vehicle. Among these, Dodge’s physical sound generator stands out as a unique effort to create a traditional “exhaust” system. However, GM has patented a device that prioritizes function over aesthetics: an emergency exhaust intended to prevent a rare but severe issue known as thermal runaway.
Typically, an electric vehicle only produces heat, making a conventional exhaust system unnecessary. Yet, excessive heat can pose a significant risk. Thermal runaway occurs when a battery, due to a defect or damage, generates more heat than its cooling system can manage, leading to a chain reaction that creates flammable gases. This phenomenon is the precursor to what many refer to as a “thermal event.”
In layman's terms, that's fire.
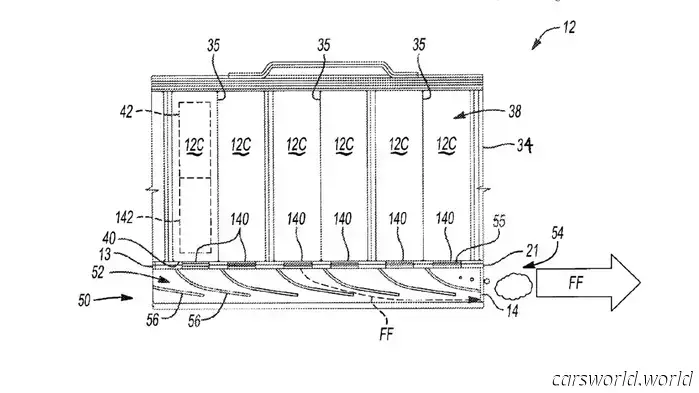
GM’s patent outlines a system designed to mitigate the risk of thermal runaway leading to a thermal event. Referring to it as an “exhaust” might be overstating it; it's more accurately described as an advanced wastegate.
The system features a series of valves and/or caps that release the hot, combustible gases produced within the malfunctioning battery cells and direct them through baffles that redirect the gases away from neighboring cells and into a central exhaust chamber, where they are vented to the atmosphere. This process reduces heat from the battery pack and removes potential ignition sources simultaneously.
While the primary fire risk originates from the EV’s battery, GM does not address the concern regarding the expulsion of combustible gases into a potentially chaotic environment following an accident. Earlier this year, Stellantis sought a patent for a similar system that included a scrubber (similar to a catalytic converter) to filter out unwanted elements from the expelled gases.
Functionally, GM's design resembles an emergency relief valve commonly found on water heaters more than a traditional internal-combustion exhaust system. Nevertheless, it qualifies as an exhaust system. Ideally, a vehicle fitted with such a system would never need to use it. However, in cases of an accident or a defective/damaged battery, it could be the difference between merely replacing a dead battery pack or having to rebuild a burned garage or home. It certainly seems promising.
Have tips? Send them to [email protected]

Other articles
 2025 Will Experience the Lowest Number of New Car Model Launches in Several Decades.
Typically, over 200 new car models are launched every four years. The upcoming forecast has decreased to 159, raising concerns among analysts.
2025 Will Experience the Lowest Number of New Car Model Launches in Several Decades.
Typically, over 200 new car models are launched every four years. The upcoming forecast has decreased to 159, raising concerns among analysts.
 A Genuine Mitsubishi Ralliart SUV Might Be Nearer Than You Anticipate | Carscoops
Mitsubishi indicates that a sporty SUV is being contemplated, inspired by motorsport and customized for various markets.
A Genuine Mitsubishi Ralliart SUV Might Be Nearer Than You Anticipate | Carscoops
Mitsubishi indicates that a sporty SUV is being contemplated, inspired by motorsport and customized for various markets.
 Rivian’s concept for a Tonneau cover awning is a fantastic example of simple yet effective innovation.
A tonneau cover for a truck that can also function as a camping awning is an excellent concept. There's no need to transport two tarp-like items when one can serve a dual purpose.
Rivian’s concept for a Tonneau cover awning is a fantastic example of simple yet effective innovation.
A tonneau cover for a truck that can also function as a camping awning is an excellent concept. There's no need to transport two tarp-like items when one can serve a dual purpose.
 You Continue Purchasing Manual Z4s, Which May Mean the GR Supra Sticks Around a While Longer Too | Carscoops
The automaker does not intend to introduce a successor to the Z4 but may continue its production until May 2026.
You Continue Purchasing Manual Z4s, Which May Mean the GR Supra Sticks Around a While Longer Too | Carscoops
The automaker does not intend to introduce a successor to the Z4 but may continue its production until May 2026.
 The Future of Maserati Uncertain as Stellantis Rushes to Develop a New Strategy | Carscoops
The head of Maserati has refuted claims that Stellantis might be putting the brand up for sale.
The Future of Maserati Uncertain as Stellantis Rushes to Develop a New Strategy | Carscoops
The head of Maserati has refuted claims that Stellantis might be putting the brand up for sale.
Here’s the Reason GM Created a Gas Exhaust for Electric Vehicles
Electric cars can indeed gain from having an exhaust system, but not in the way you might expect.
