
These Japanese Automotive Manufacturers Are Investing in Clean Fuel Derived from Grass and Paper | Carscoops
Your next vehicle may soon utilize a new mix of ethanol and traditional gasoline.
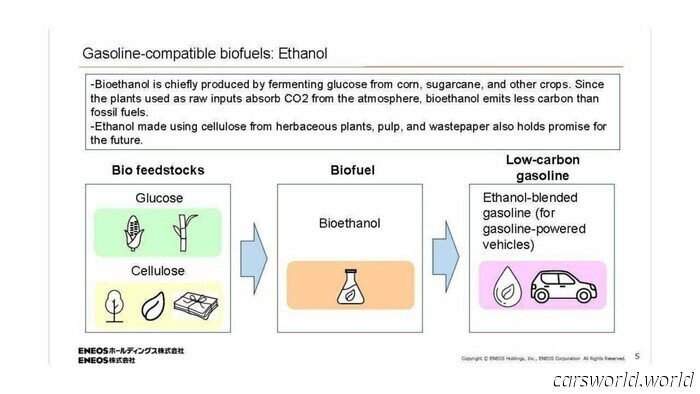
ENEOS is working on developing ethanol fuel derived from grass, wood, and recycled paper.
Nissan, Mazda, Subaru, and Toyota are advocating for low-carbon fuels for both racing and road applications.
Japan's Super Taikyu Series is set to utilize new plant-based fuel alternatives in the upcoming season.
As the automotive sector seeks ways to lower emissions, there is skepticism about whether fully electric powertrains are the only solution. While many manufacturers are heavily focusing on battery-electric vehicles, a coalition of Japanese automakers, including Nissan, Mazda, Subaru, and Toyota, is pursuing a different strategy.
In collaboration with the petroleum giant ENEOS, they are developing a low-carbon gasoline alternative that will make its debut in the ST-Q class of Japan's Super Taikyu racing series. Eventually, this type of fuel might power everyday vehicles.
This fuel comprises a combination of plant-derived bioethanol mixed with regular gasoline. Although it may seem similar to existing ethanol and gasoline blends like E85, which have been available for several years, Japanese companies are exploring a unique approach.
Instead of using crops like corn or sugarcane, typically involved in ethanol production, ENEOS is investigating methods to produce ethanol from non-food biomass. This distinction is crucial since current biofuels rely on agricultural land and resources, which limits the volume of fuel that can be produced. ENEOS is researching alternative sources such as wood, grass, and recycled paper to generate ethanol that can be blended with gasoline.
The Future of Fuel
Vehicles utilizing this low-carbon fuel will be the first to compete in the Super Taikyu Series with a domestically produced alternative to conventional gasoline.
“I believe we’re moving towards a global consensus that, while BEVs and hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCEVs) contribute significantly, HEVs and internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles can also play a role in reducing CO2 emissions,” stated Yuichiro Fujiyama, ENEOS Chief Technology Officer, in an interview with Toyota Times.
“To further cut emissions, we must tackle the CO2 emitted by the liquid fuels used in vehicles. We believe greater emphasis should be placed on e-fuels, synthetic fuels, and the biofuels currently utilized by some ST-Q cars,” he added.
Inspired by Brazil
The automakers pointed to Brazil's extensive use of biofuels as a model that Asia could emulate. In Brazil, many cars are offered with flex-fuel capability, and local subsidies make ethanol blends more affordable than standard gasoline. ENEOS does not necessarily believe that subsidies are the solution to making biofuels more widespread, asserting that “the key factor is whether people are willing to invest in the fight against global warming, even if it comes at a higher personal cost.”
“As I have mentioned numerous times, automobiles are remarkable products,” added Subaru Chief Technology Officer Tetsuo Fujinuki. “Thus, we need to leverage our diversity while tackling environmental issues, such as reducing exhaust emissions and achieving carbon neutrality. I believe that carbon-neutral fuels play an essential role in this endeavor.”
While electric vehicles often dominate discussions, initiatives like this serve as a reminder that advancements in combustion fuels remain significant, particularly in areas where electrification may not be a viable option.



Other articles
 Police Stop Robotaxi for Making an Illegal Turn, But There's No Driver in the Seat | Carscoops
In California, autonomous vehicles are currently not subject to fines, but this exemption will be lifted in July 2026.
Police Stop Robotaxi for Making an Illegal Turn, But There's No Driver in the Seat | Carscoops
In California, autonomous vehicles are currently not subject to fines, but this exemption will be lifted in July 2026.
 Walmart's incredibly affordable Amazon Prime Day tool kit offers are appealing if you're not picky about brands.
Walmart has reduced the prices of certain already affordable tool kits by 50%.
Walmart's incredibly affordable Amazon Prime Day tool kit offers are appealing if you're not picky about brands.
Walmart has reduced the prices of certain already affordable tool kits by 50%.
 Les ventes du Jeep Wagoneer sont en chute libre. Est-il trop tard pour le sauver ?
Jeep aims to revitalize Wagoneer sales by introducing two new packages.
Les ventes du Jeep Wagoneer sont en chute libre. Est-il trop tard pour le sauver ?
Jeep aims to revitalize Wagoneer sales by introducing two new packages.
 Chevy Revamped Its Most Affordable Global Models with a Digital Update and Unremarkable Designs | Carscoops
Six years post-launch, the Onix family is receiving significant enhancements.
Chevy Revamped Its Most Affordable Global Models with a Digital Update and Unremarkable Designs | Carscoops
Six years post-launch, the Onix family is receiving significant enhancements.
 Lexus Tied Two Tennis Players to the Roof and Then Drove Around | Carscoops
The pair exchanged the ball repeatedly, establishing two records along the way.
Lexus Tied Two Tennis Players to the Roof and Then Drove Around | Carscoops
The pair exchanged the ball repeatedly, establishing two records along the way.
 Why the 2026 Mazda CX-5 Continues to Feature a Traditional Six-Speed Transmission
In the age of eight-speed automatic transmissions, Mazda continues to utilize a six-speed gearbox in the new CX-5 as it effectively fulfills its purpose.
Why the 2026 Mazda CX-5 Continues to Feature a Traditional Six-Speed Transmission
In the age of eight-speed automatic transmissions, Mazda continues to utilize a six-speed gearbox in the new CX-5 as it effectively fulfills its purpose.
These Japanese Automotive Manufacturers Are Investing in Clean Fuel Derived from Grass and Paper | Carscoops
Your next vehicle might utilize a new mixture of ethanol and regular gasoline.
